Table of Contents
Speech Theraphttps://shinebrightautism.org/2025/03/19/types-of-speech-therapy/y Techniques
Speech therapy techniques are essential interventions for individuals experiencing communication impairments. The application of these methodologies facilitates improved speech and language abilities. It is recognized that effective communication is a cornerstone of social, educational, and vocational success. Consequently, speech therapy addresses diverse disorders, including articulation, fluency, and voice-related challenges.
The importance of these interventions is underscored by their capacity to enhance an individual's quality of life. Consider the impact of acquired communication disorders; speech therapy can serve as a critical component of rehabilitation. The restoration of communicative competence directly influences an individual's capacity to participate fully in society.
Understanding Speech Therapy and Its Importance
Speech therapy encompasses a range of clinical practices aimed at ameliorating communication deficits. This field provides support for individuals with various speech and language disorders. The significance of this discipline is rooted in the fundamental role of communication in human interaction.
Proficiency in language enables effective social engagement, academic achievement, and professional advancement. For individuals with communication impairments, speech therapy can be instrumental in mitigating the impact of these challenges. It is understood that the ability to articulate needs and express thoughts is integral to an individual's well-being. Therefore, speech therapy represents a vital service in the restoration and development of communicative abilities.
Core Techniques Used in Speech Therapy
Speech therapy utilizes a variety of core techniques, each designed to address specific communication challenges. These techniques can be broadly categorized as follows:
Core Techniques Used in Speech Therapy
| Articulation Therapy: Fixes sound errors. Language Intervention: Improves vocabulary and grammar. Fluency Therapy: Reduces stuttering. Voice Therapy: Treats voice problems. Cognitive-Communication Therapy: Improves thinking skills for communication. Swallowing Therapy: Helps with swallowing issues. |
These core techniques are often integrated and adapted to meet the individual needs of each client. The application of these methods is crucial for enhancing communication skills and improving overall quality of life.
Articulation Therapy: Correcting Speech Sounds
Articulation therapy is a clinical intervention focused on the precise production of phonemes. The objective is to rectify misarticulations and establish accurate speech sound production. This process involves the systematic identification and correction of errors in sound articulation. Therapeutic strategies include repetitive exercises, visual aids, and auditory feedback.
The focus is on developing precise articulatory movements through targeted practice. The intended outcome is the attainment of clear and intelligible speech. This therapeutic approach is instrumental in addressing phonological disorders and enhancing communication effectiveness.
Language Intervention Strategies for Better Communication
Language intervention strategies focus on improving both receptive and expressive language skills. A variety of methods are employed to address these areas. Receptive language, or understanding, is enhanced through activities that build vocabulary and comprehension. Expressive language, or speaking, is targeted through exercises that improve sentence structure and narrative skills.
Vocabulary Development:
- Use of picture cards and real objects to teach new words.
- Contextual learning through stories and conversations.
- Employing word association and categorization tasks.
Grammar and Syntax Improvement:
- Sentence building activities using visual aids.
- Modeling correct sentence structure and providing feedback.
- Interactive games that focus on verb tenses and pronouns.
Narrative Skills:
- Story retelling and sequencing activities.
- Developing the ability to describe events and experiences.
- Using visual supports to aid in story comprehension and production.
Pragmatic Language:
- Role-playing social situations.
- Teaching turn-taking and conversational skills.
- Addressing nonverbal communication cues.
These strategies are tailored to the individual's needs. The goal is to improve the ability to understand and express language effectively. A strong foundation for communication is built.
Fluency Shaping Methods to Overcome Stuttering
Fluency shaping methods represent a set of techniques aimed at modifying speech patterns to reduce or eliminate stuttering. These approaches focus on establishing new, fluent speech behaviors.
Prolonged Speech:
- Involves stretching syllables to slow down the rate of speech.
- Promotes smoother transitions between words.
- Reduces the likelihood of stuttering moments.
Light Articulatory Contacts:
- Emphasizes gentle contact between articulators (lips, tongue, teeth).
- Reduces tension in the speech musculature.
- Minimizes the occurrence of blocks and repetitions.
Easy Onset:
- Focuses on initiating speech with a relaxed vocal fold posture.
- Prevents abrupt starts that can trigger stuttering.
- Promotes a smooth flow of speech from the beginning of utterances.
Continuous Phonation:
- Maintaining a continuous flow of voice throughout speech.
- Minimizes pauses and breaks in speech.
- Enhances the rhythm and fluency of speech.
These methods are implemented systematically, with a focus on gradually increasing the complexity of speech tasks. The goal is to establish fluent speech patterns that can be generalized to everyday communication situations. These techniques are a vital part of helping those that struggle with fluency.
Voice Therapy for Stronger and Healthier Vocalization
Voice therapy addresses disorders affecting vocal quality, pitch, and loudness. It aims to restore healthy vocal function through targeted exercises and techniques.
- Vocal Hygiene Education:
- Provides instruction on practices that promote vocal health, such as hydration and avoidance of irritants.
- Addresses factors contributing to vocal strain and misuse.
- Emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle for optimal vocal function.
- Vocal Function Exercises:
- Involves systematic exercises to strengthen and coordinate vocal muscles.
- Targets vocal fold flexibility and endurance.
- Improves vocal efficiency and reduces vocal fatigue.
- Resonance Therapy:
- Focuses on optimizing resonance, or the way sound vibrates in the vocal tract.
- Addresses issues related to hypernasality or hyponasality.
- Enhances vocal clarity and projection.
- Muscle Tension Reduction Techniques:
- Employs relaxation exercises to reduce tension in the neck and laryngeal muscles.
- Addresses muscle tension dysphonia.
- Promotes a more relaxed and efficient vocal production.
- Pitch Modification:
- Addresses situations where pitch is too high, too low, or monotonous.
- Teaches techniques to control and vary pitch.
- Helps to achieve a pitch that is appropriate for the individual's age and gender.
These interventions are implemented to achieve stronger and healthier vocalization, therefore improving the quality of life of the individual.
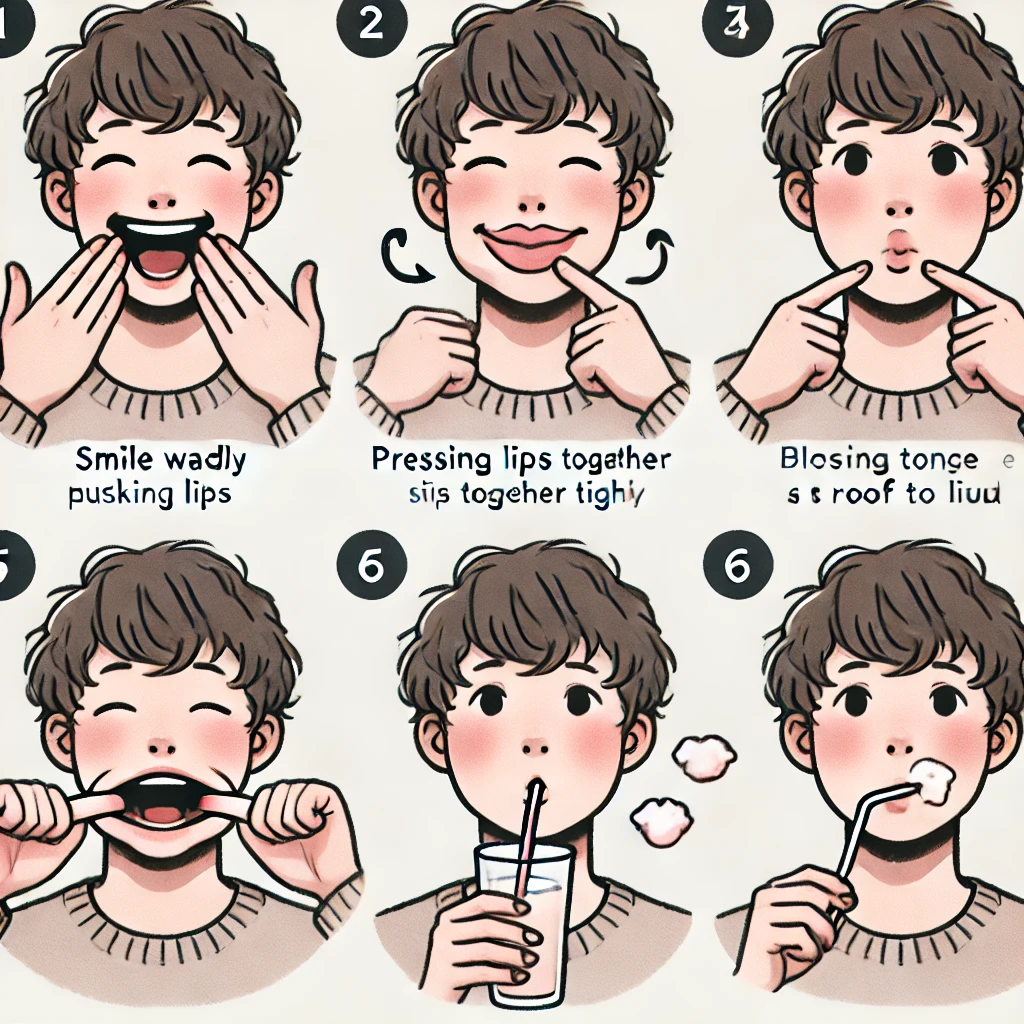
Oral Motor Exercises to Strengthen Speech Muscles
Oral motor exercises target the muscles involved in speech production. These exercises are designed to improve muscle strength, coordination, and range of motion.
- Lip Exercises:
- Involve activities such as lip pursing, lip spreading, and lip rounding.
- Strengthen the muscles responsible for lip closure and articulation.
- Improve the production of bilabial sounds (e.g., /p/, /b/, /m/).
- Tongue Exercises:
- Include activities such as tongue protrusion, tongue retraction, and lateral tongue movements.
- Strengthen the muscles responsible for tongue elevation, depression, and lateralization.
- Improve the production of lingual sounds (e.g., /t/, /d/, /l/, /s/, /z/).
- Jaw Exercises:
- Involve activities such as jaw opening, jaw closing, and lateral jaw movements.
- Strengthen the muscles responsible for jaw stability and movement.
- Improve overall articulation clarity.
- Cheek Exercises:
- Involves activities such as cheek puffing, and cheek retraction.
- Strengthen the muscles of the cheeks.
- Improves the ability to contain air in the oral cavity, which is important for speech.
- Palatal Exercises:
- Involves exercises that target the soft palate.
- Improves palatal closure, which is vital for appropriate nasal resonance.
These exercises are implemented to improve the function of the articulators, leading to clearer and more precise speech. It is important to note, that while Oral motor exercises are used, there is some debate concerning their overall effectiveness, when used alone, to treat speech sound disorders. It is important to involve a qualified Speech language pathologist when conducting these types of exercises. For those facing more severe communication limitations, Alternative and Augmentative Communication (AAC) methods can provide vital tools.
Alternative and Augmentative Communication (AAC) Methods
Alternative and Augmentative Communication (AAC) methods provide tools and strategies for individuals with severe communication impairments. These methods supplement or replace spoken or written communication.
| AAC System Type | Description | Examples |
| Unaided AAC Systems | · Rely on the user's body to convey messages. · Include sign language, gestures, and facial expressions. · Require no external equipment. | Sign language, gestures, facial expressions. |
| Aided AAC Systems | · Utilize external devices or tools. | |
| Low-Tech AAC | Simple, non-electronic communication aids. | · Picture communication boards. · Symbol systems. · Written communication. |
| High-Tech AAC | Electronic devices that generate speech or text. | · Speech-generating devices (SGDs). · Tablets and computers with communication software. · Eye-tracking systems. |
| Symbol Systems | Visual representations used to convey meaning. | · Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS). · SymbolStix. · Widgit Symbols. |
| Communication Strategies | Focus on effective message delivery. | · Partner-assisted scanning. · Predictive text. · Topic boards. |
| Access Methods | Determine how the user interacts with the AAC system. | · Direct selection (touchscreen). · Scanning. · Switches. |
AAC methods are implemented to provide individuals with effective communication tools. These systems are selected and adapted to meet the specific needs and abilities of each user, therefore expanding their ability to communicate.
Speech Therapy at Home: Effective DIY Techniques
Home-based speech therapy can supplement professional sessions, providing consistent practice. These DIY techniques can be integrated into daily routines.
- Reading Aloud:
- Enhances articulation and fluency.
- Select age-appropriate books.
- Focus on clear pronunciation and pacing.
- Picture Card Activities:
- Builds vocabulary and expressive language.
- Use flashcards with images.
- Encourage sentence formation.
- Storytelling:
- Develops narrative skills.
- Retell familiar stories.
- Create new stories together.
- Interactive Games:
- Improves language comprehension.
- Use board games or apps.
- Focus on following directions.
- Daily Conversation Practice:
- Reinforces communication skills.
- Engage in regular conversations.
- Encourage detailed responses.
- Sound Repetition Exercises:
- Targets articulation errors.
- Repeat specific sounds or words.
- Use a mirror for visual feedback.
- Singing:
- Improves vocal control and rhythm.
- Sing familiar songs.
- Focus on clear enunciation.
Consistent application of these techniques can support speech development at home. It is important to remember that these techniques are to be used in conjunction with professional therapy.

Choosing the Right Speech Therapist: What to Look For
Selecting an appropriate speech therapist is crucial for effective intervention. Several factors should be considered when making this decision.
- Credentials and Certifications:
- Verify that the therapist holds a Master’s degree in Speech-Language Pathology.
- Confirm certification from relevant professional organizations.
- Check for state licensure.
- Experience and Specialization:
- Inquire about the therapist's experience with specific communication disorders.
- Determine if the therapist specializes in the area of concern.
- Ask about their experience working with individuals of a similar age.
- Communication and Rapport:
- Assess the therapist's ability to communicate clearly and effectively.
- Observe their interaction style and rapport with the client.
- Consider if the therapist is empathetic and patient.
- Treatment Approach:
- Discuss the therapist's treatment philosophy and methods.
- Determine if the approach aligns with the client's needs and preferences.
- Inquire about the use of evidence-based practices.
- Availability and Accessibility:
- Consider the therapist's availability and scheduling options.
- Evaluate the location and accessibility of the therapy setting.
- Inquire about telehealth options, if applicable.
- Collaboration and Communication:
- Determine if the therapist collaborates with other professionals, such as teachers or physicians.
- Inquire about the frequency and method of communication with caregivers.
- Find out how progress will be monitored and reported.
- Client Comfort:
- Observe how comfortable the individual is with the potential therapist.
- A comfortable enviornment promotes better therapy outcomes.
Careful consideration of these factors will aid in selecting a qualified and compatible speech therapist.
Final Thoughts: Taking the First Step Towards Clearer Speech
Commencing speech therapy represents a significant step towards improved communication. The journey towards clearer speech requires dedication and consistent effort. It is important to recognize that progress may vary, and patience is essential.
- Early Intervention: Addressing communication challenges early can yield substantial benefits.
- Consistent Practice: Regular practice of therapy techniques is crucial for progress.
- Collaboration: Working closely with a speech therapist and caregivers enhances outcomes.
- Positive Mindset: Maintaining a positive outlook and celebrating small victories fosters motivation.
- Individualized Approach: Recognizing that each individual's needs are unique ensures effective therapy.
- Lifelong Skills: Speech therapy can provide lifelong skills that enhance quality of life.
- Support System: Building a strong support system, including family and friends, provides encouragement.
Taking the initial step towards speech therapy can be transformative. It is a process that empowers individuals to overcome communication barriers and achieve their full potential.

